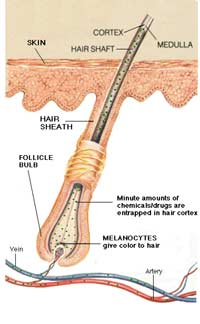
Urine is the most widely used specimen for drugs of abuse testing because of the advantages of large specimen volume and relatively high drug concentrations that render drug detection comparatively easier than in other specimens. Drugs in urine are detectable by standard drug test on urine between 1-3days. Urine sample of individual is under tightly controlled condition.
The person will likely be asked to go to a testing facility where he or she will need to remove street clothing and put on a hospital gown. This ensures that a clean sample from someone else is not removed in to the testing center and substituted fort the subject's urine.
Once they changed into the gown, he or she is accompanied to the testing area. This is a washroom where the water in the toilet tank has been dyed so that an attempt to water down the sample by adding toilet water will be quite obvious. The water supply at the sink will have been shut off so that a person will not intended to use that source of liquid to alter the sample. A staff member will be waiting nearby to take the sample once it has been provided. The standard protocol is to test it to confirm that the temperature is consistent with normal body temperature.
A negative reading on drug test doesn’t mean that there is no presence of heroin in the body. According to Mandatory Guidelines for Federal Workplace Drug Testing Program, it simply means that sample taken didn't record a level higher than the threshold.
The cutoff value is 2000 nanograms per milliliter. It is usually repeated when the initial urine test is positive for drugs, including horse. If a second result have reach the cutoff value 2000 ng/ml means it is positive and the subject will be facing consequences, and none of them will be good.
ADVANTAGES
• It has the highest assurance of reliable results
• It is least expensive
• On-site testing kits are available
• Acceptable in court to withstand legal challenge
DISADVANTAGES
• It is exposed to adulteration or substitution
• It is does not need dose-concentration relationship
• The test are sometimes viewed as psychologically invasive or embarrassing
• Biological hazard for specimen handling and shipping to laboratory
Window of detection: Typically 1 to 3 days, except for cannabis (1 day to 2 weeks)
Urine Drug Specimen Collection Procedure
1. The collector must wash hands and wears gloves.
2. The collector must add bluing agent (dye) to the toilet water reservoir to stop from an adulterated specimen.
3. The collector must removes any source of water other than toilet by applying a tape to the the toilet lid and faucet handles.
4. The donor must give photo identification from employer representative.
5. The collector should complete the step 1 of the chain of custody (COC) form and has the donor sign the form.
6. The donor leaves his or her bag or purse outside the collection area to avoid the contaminating the urine by the any substances.
7. The donor should washes his or her hands and receives a specimen cup.
8. The collector must observe for unauthorized water use. The collector must remains in the restroom but outside the stall, unless a witnessed collection is requested.
9. The donor hands specimen cup to the collector. Transfer is documented.
10. The collector checks the required amount volume, it should be 30–45 mL and for abnormal color of urine.
11. The collector must check the temperature strip on the specimen cup reads. It should be beyond 32.5C to37.7C. The collector records on the Chain of (Step 2) form, the in-range temperature of the specimen . If the specimen temperature is out of range this means the specimen is questionable to have been diluted or adulterated. A new specimen must be collected and a supervisor notified.
12. The specimen must remain in the sight by the donor and collector at all times.
13. The collector leave the specimen identification strips from the
Chain of Custody form and attach them on the capped bottle, covering both sides of the cap.
14. The donor initials the specimen bottle seals.
15. The date and time are labelled on the seals.
16. The donor completes step 4 on the Chain of Custody form.
17. The collector completes step 5 on the Chain of Custody form.
18. Each time the specimen is handled, transferred, or placed in storage, every individual must
be identified and the date and purpose of the change recorded.
19. The collector follows laboratory-specific instructions for packaging the specimen bottles
and laboratory copies of the Chain of Custody form.
20. The collector distributes the Chain of Custodycopies to appropriate personnel.
Urine Drug Test Kit for Heroin
Opiate (HEROINE, MORPHINE) Cassette Drug Urine Test Kit
It is simple, accurate and reliable. All tests are CE Marked and FDA Approved, with an accuracy level of 99%. It is easy to follow instructions.
PRINCIPLE OF THE TEST
The test is a competitive binding immunoassay in which drug and drug metabolites in a urine sample compete with immobilized drug conjugate for limited labeled antibody binding sites. By utilizing antibodies that are specific to different drug classes, the test permits independent, simultaneous detection of two drugs from a single sample. The approximate run time is 5 minutes. It's cutoff value is 2000 nanograms per milliliter.